Initial MBS support in the 5GC
This tutorial showcases the current features present in the 5G-MAG MBS implementation. You can check out the video to see more details or follow the write-up tutorial.
Tutorial video
Prerequisites
Before starting with this tutorial please follow the Docker installation instructions for the 5MBS stack. This tutorial assumes that you have cloned the rt-mbs-examples repository and started the 5MBS Docker images with the internal deployment mode.
You can verify that all Docker containers are running by executing docker ps -a on the host machine.
Description
In this tutorial an MBS Broadcast Session will be created in order to send traffic from the AS to a multicast group ( Source-Specific Multicast - SSM) and see the traffic going through the 5G Core and leaving the MB-UPF (Lower Layer SSM) reaching the gNB. The basic architecture of the different components/containers is depicted in the illustration below.
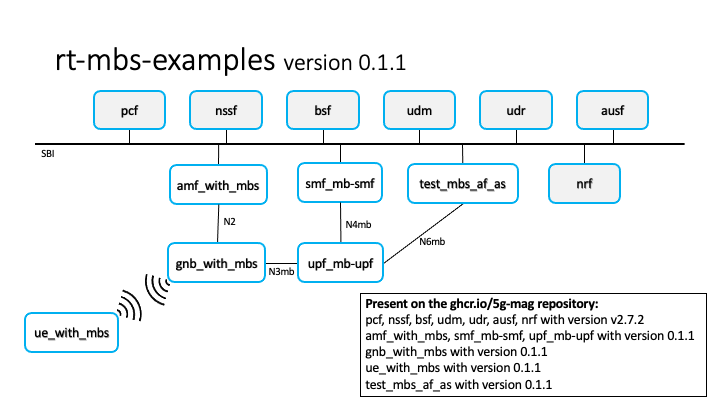
Note: Currently receiving multicast traffic on the gNB is not supported. However while performing the MBS Session setup you can sinaling between between the AMF and the gNB through the N2 interface.
In order to create an MBS Broadcast Session a TMGI will be used as identifier alongside an SSM address. This will be the address that the AS will use to send the multicast traffic to the MB-UPF through the N6mb interface. The LLSSM is the lower layer SSM that the MB-UPF will use to reach the gNBs acting as recepient of the multicast traffic.
Important note: Currently, there is a limit of 20 MBS Sessions per MB-UPF. The range of IP multicast addresses being used for the MB-UPF to forward the multicast traffic to the gNB using the LLSSM is
239.0.0.4-239.0.0.24. It is recommended to start the range for the SSM on the IP multicast address239.0.0.25onwards.
Note that this tutorial makes use of methods to manage MBS Session and TMGI as described in this tutorial.
Step 1: Creating an MBS Session
Connect to the shell of the test_mbs_af_as container:
# Connect to the test_mbs_af_as container
docker exec -it test_mbs_af_as sh
From the test_mbs_af_as container execute the following command to create an MBS session. Replace <af_as_container_ip> with the IP of the test_mbs_af_as container. You can derive the IP by calling ip address in the shell and copying the eth0 interface address. In addition, replace <n6mb_ip_multicast_destination_address> with a valid multicast address such as 239.0.0.25 or higher.
# MBS Session Create request with TMGI allocate: /nmbsmf-mbssession/v1/mbs-sessions with multicast source
curl --http2-prior-knowledge \
--request POST \
--header "Content-Type: application/json" \
--data '{ "mbsSession": { "ssm": { "sourceIpAddr": { "ipv4Addr": "<af_as_container_ip>" }, "destIpAddr": { "ipv4Addr": "<n6mb_ip_multicast_destination_address>" } },"tmgiAllocReq": true, "serviceType":"BROADCAST" } }' \
smf-mb-smf.5g-mag.org:80/nmbsmf-mbssession/v1/mbs-sessions
This command will create an MBS Session of type BROADCAST, specifying the SSM address from which the MB-UPF will receive the traffic from test_mbs_af_as. With the parameter tmgiAllocReq set to true, the request also tells the MB-SMF to create a TMGI for this MBS Session.
Step 2: MB-UPF traffic configuration
In order for the MB-UPF to receive the traffic being sent to this multicast group (SSM) and then forward it to the LLSSM, we need to connect to the MB-UPF container:
# Connect to the MB-UPF container
docker exec -it upf_mb-upf sh
And then execute the following command (eplace n6mb_ip_multicast_destination_address with the multicast address that you chose in the previous step, e.g. 239.0.0.25) to configure the MB-UPF:
# Execute this command inside the MB-UPF container
smcroutectl add eth0 <n6mb_ip_multicast_destination_address> ogstun
This command will update the MFC of the MB-UPF to receive the traffic for the multicast group <n6mb_ip_multicast_destination_address> and forward it internally using the ogstun interface.
After all of this is configured, the MB-UPF has been configured through PFCP to forward the traffic received to the LLSSM. The first LLSSM created uses the multicast destination address 239.0.0.4 and random C-TEID.
Step 3: Sending multicast IP packets
Through the test_mbs_af_as with IP address <af_as_container_ip> you can send an IP packet to the multicast destination <n6mb_ip_multicast_destination_address>. This causes the MB-UPF to forward the traffic using GTPU to the LLSSM
To verify that the traffic is being forwarded to the LLSSM execute the following command on your host machine:
tcpdump -i br-5g-mag udp port 2152
Connect to test_mbs_af or use the previously connected terminal:
# Connect to test_mbs_af or use the previously connected terminal
docker exec -it test_mbs_af_as sh
Then send traffic from the test_mbs_af_as container (replace <af_as_container_ip> and <n6mb_ip_multicast_destination_address> with the respective IP addresses):
sendip -p ipv4 -is <af_as_container_ip> -id <n6mb_ip_multicast_destination_address> upf-mb-upf.5g-mag.org
Note: When the gNB part is done, this traffic will be received by the gNBs configured to listen to the LLSSM and forward it to the UEs using PTM.